WINTHS®
Software solution for calculating thermal stresses in glass by solar radiation
Professional calculation
of thermal loads on glass surfaces
Powerful functionality
to minimize the risk of glass breakage
WINTHS®
WINTHS® is the software solution for simple and user-friendly calculation of the climatic conditions acting on glass panes, taking into account geographical location and historical weather data in accordance with NF DTU 39 P3.
WINTHS® makes it possible to determine the occurring thermal stresses on glass surfaces in advance with regard to extreme weather data, thus drastically minimizing the risk of glass breakage.
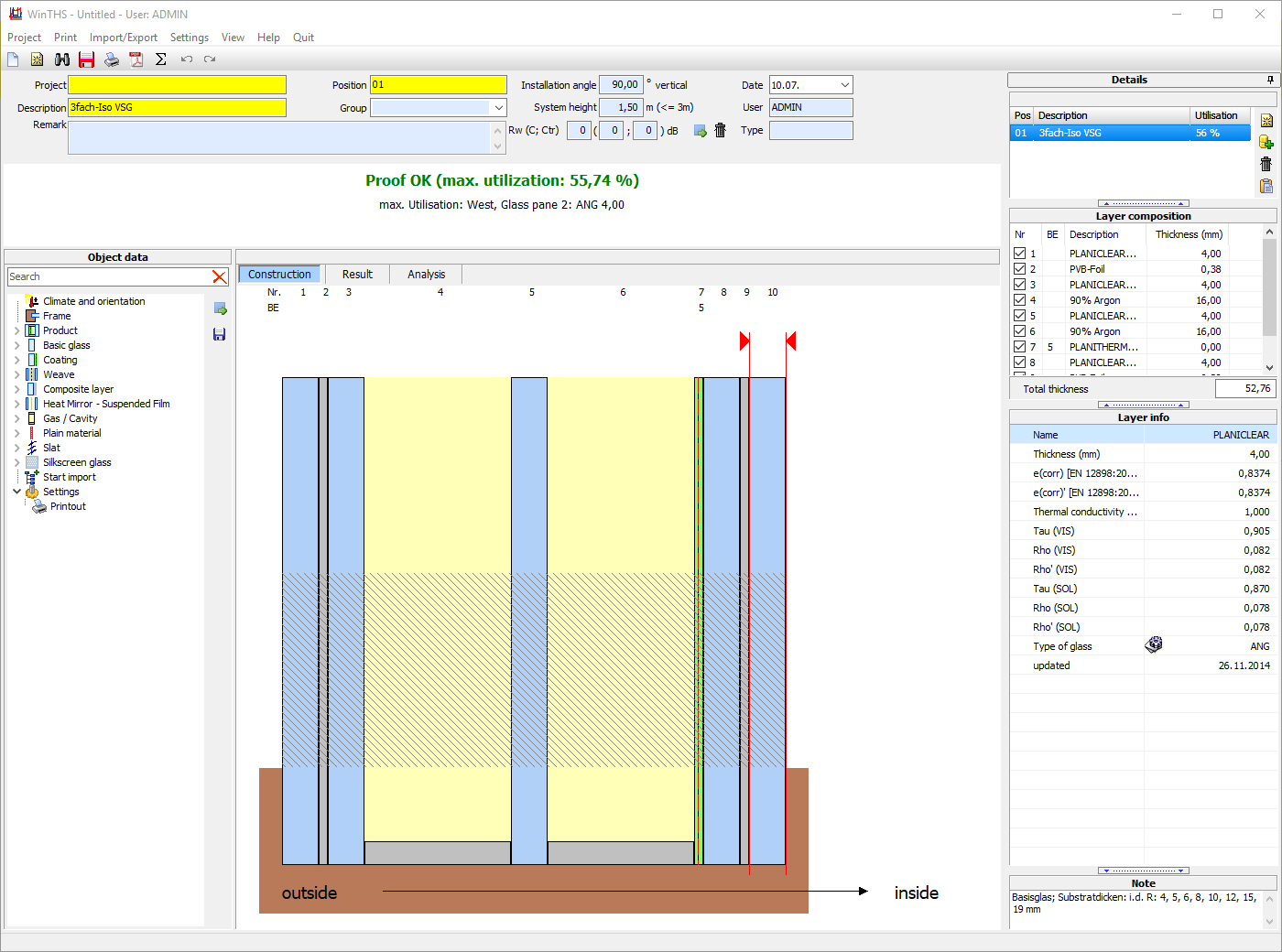
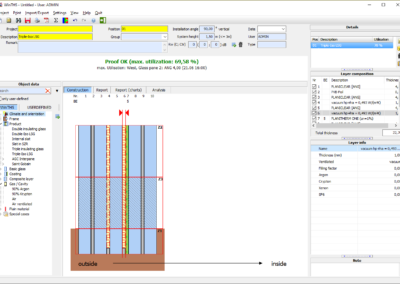
In the calculation, WINTHS® takes into account a wide range of factors that influence the thermal loads on glass surfaces. The pane structure is fundamental: glass quality, edge quality, gaps, gas fillings, type and thickness of the frame and its thermal inertia.
These values are set in relation to the prevailing climatic conditions at the installation site. The basis for this can be existing climate data (average and extreme values) for this region, as well as freely selectable values.
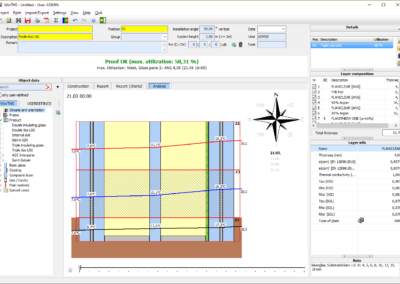
The results are displayed in the form of graphs. In addition, all relevant calculation results are displayed to the user in a detailed report, including a summary of whether the respective glass structure satisfies the locally prevailing temperature fluctuations.
Features
- Calculation according to NF DTU 39 P3
- Extensive database with products from international glass and sun protection manufacturers
- Calculation of any pane structures and shading arrangements
- Detailed thermal modeling of the frame for low, medium or high thermal inertia
- Over 3600 international climate data sets available. Display of outdoor temperatures, solar radiation, cloud cover, air quality and ambient albedo
- Comprehensive mapping of properties and installation conditions of the glazing: orientation, partial shading, coatings, printing, storage, processing of the glass edg
- All special cases in accordance with NF DTU 39 P3: external solar shading, internal opaque elements, sliding elements, projecting glazing, wall insertion, heat sources
- Graphical evaluation in diagram form, with false colors and as time-resolved animation
- PDF reports for documentation and communication of proofs
- Structured saving of projects in the SommerGlobal® database and intuitive data exchange with the SommerGlobal® applications WINSLT®, GLASGLOBAL® and WINISO®
Test our demo version!
Why WINTHS®?
- Results are internationally recognized
- Extremely user-friendly operation
- Reliable partner for long-term customer satisfaction
- Market-ready solutions even before the relevant laws and standards are passed, along with ongoing updates - our solutions are always up to date
Test our demo version!
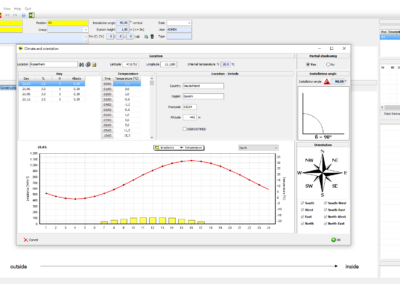
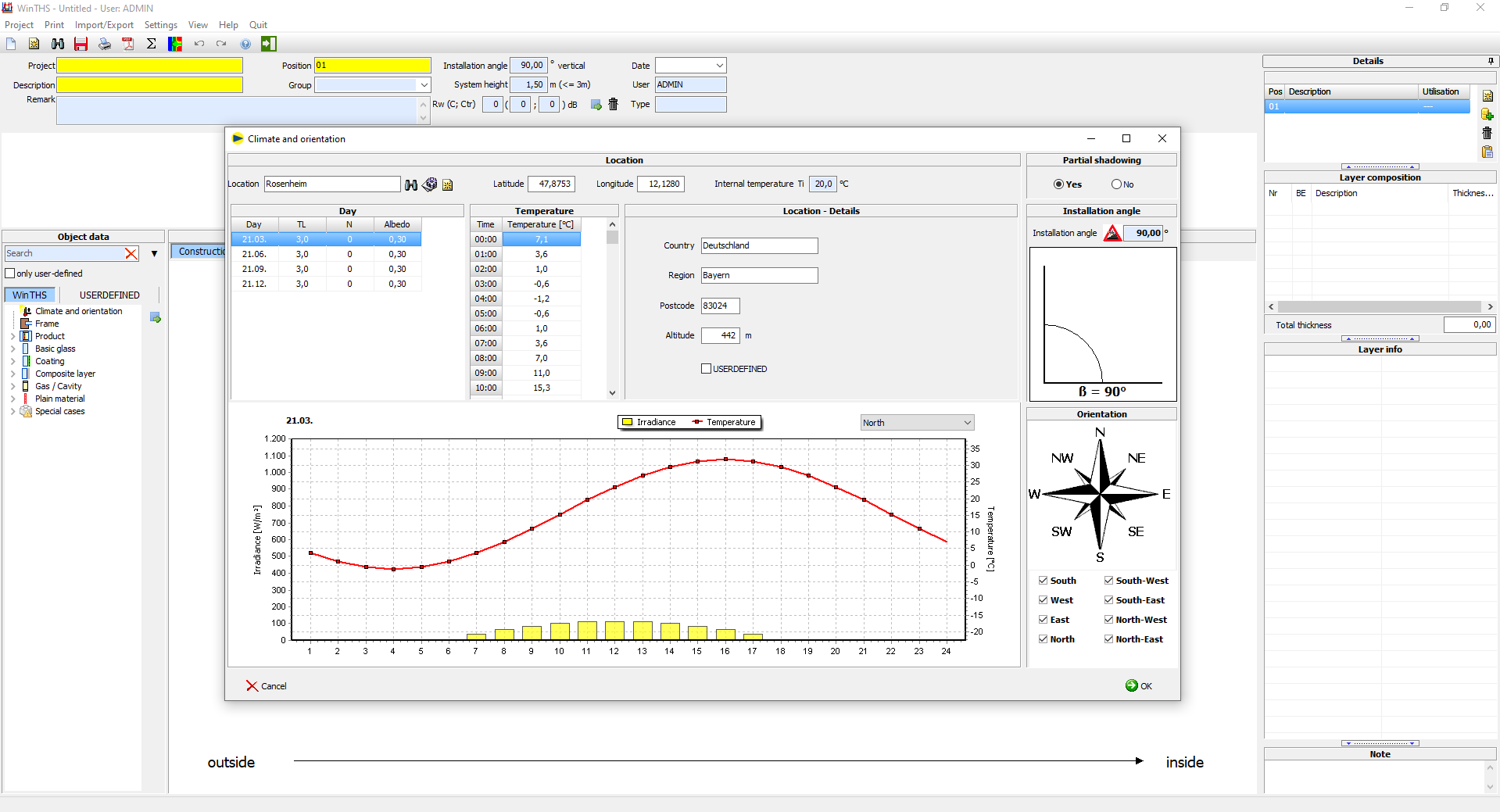
Climate & orientation
- Location
Definition of the location from which the outdoor temperatures and irradiance levels are determined for the specified days during the calculation. WINTHS® provides over 3600 climate data sets worldwide for this purpose. - Partial shading
A sun visor, a canopy, a loggia or the building structure can cast a temporary or permanent shadow on the glazing. This effect is taken into account when calculating the thermal stress. - Installation angle
Installation angle in relation to the horizontal for vertical, horizontal and inclined glazing. - Orientation
Alignment of the glazing in relation to the north direction. Automatic calculation for up to 8 cardinal points.
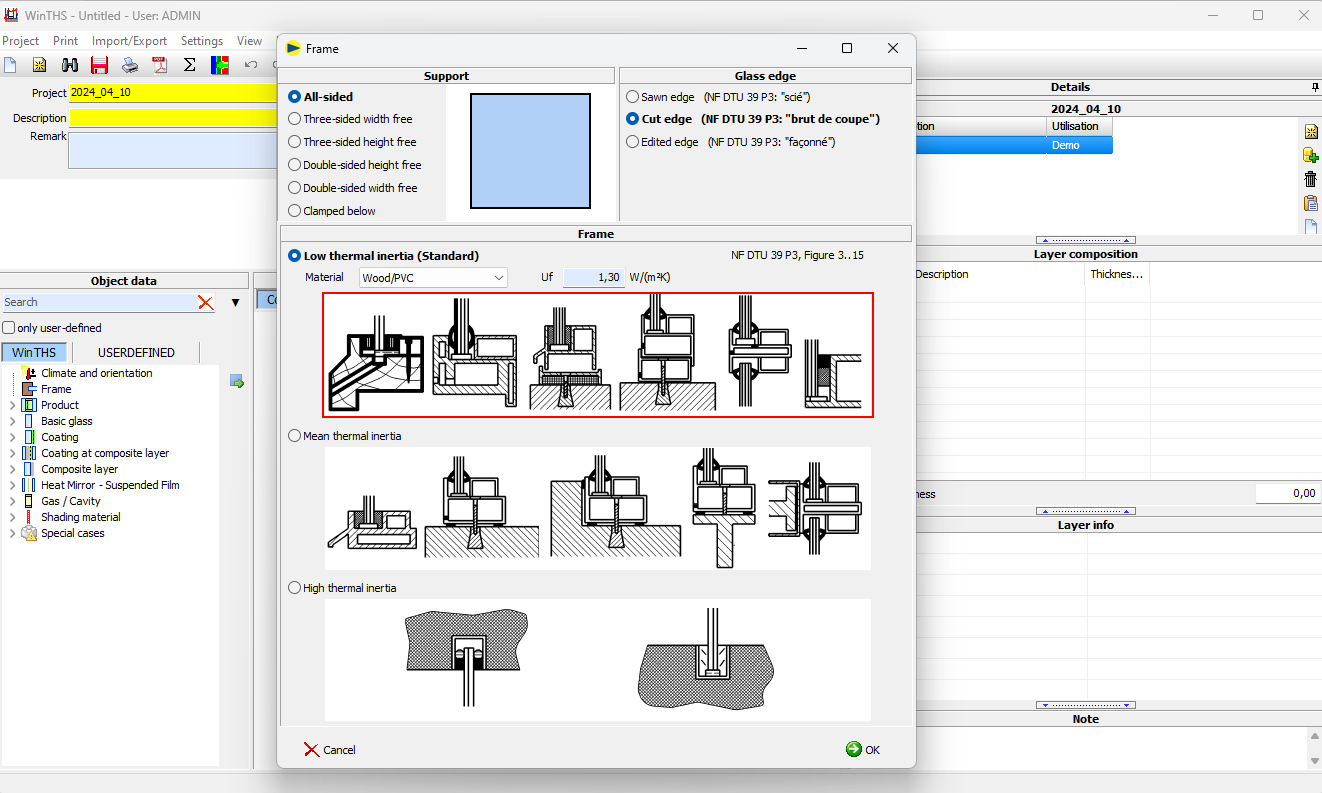
Frame
- Bearing
In accordance with NF DTU 39 P3, WINTHS® distinguishes between all-sided support and constructions with one or more free edges of the glazing. This has an effect on the permissible stress through the coefficient ka (NF DTU 39 P3 Tab.9). - Glass edge
The risk of crack propagation depending on the processing of the glass edge (sawn, cut, machined) is included in the calculation of the permissible stress through the coefficient kv in accordance with NF DTU 39 P3 Tab. 11. - Frame type
The frame is characterized by its thermal inertia (generally low inertia), material and frame U-value Uf. This information is used to determine the temperature profile of the glass in the frame (zone 1).
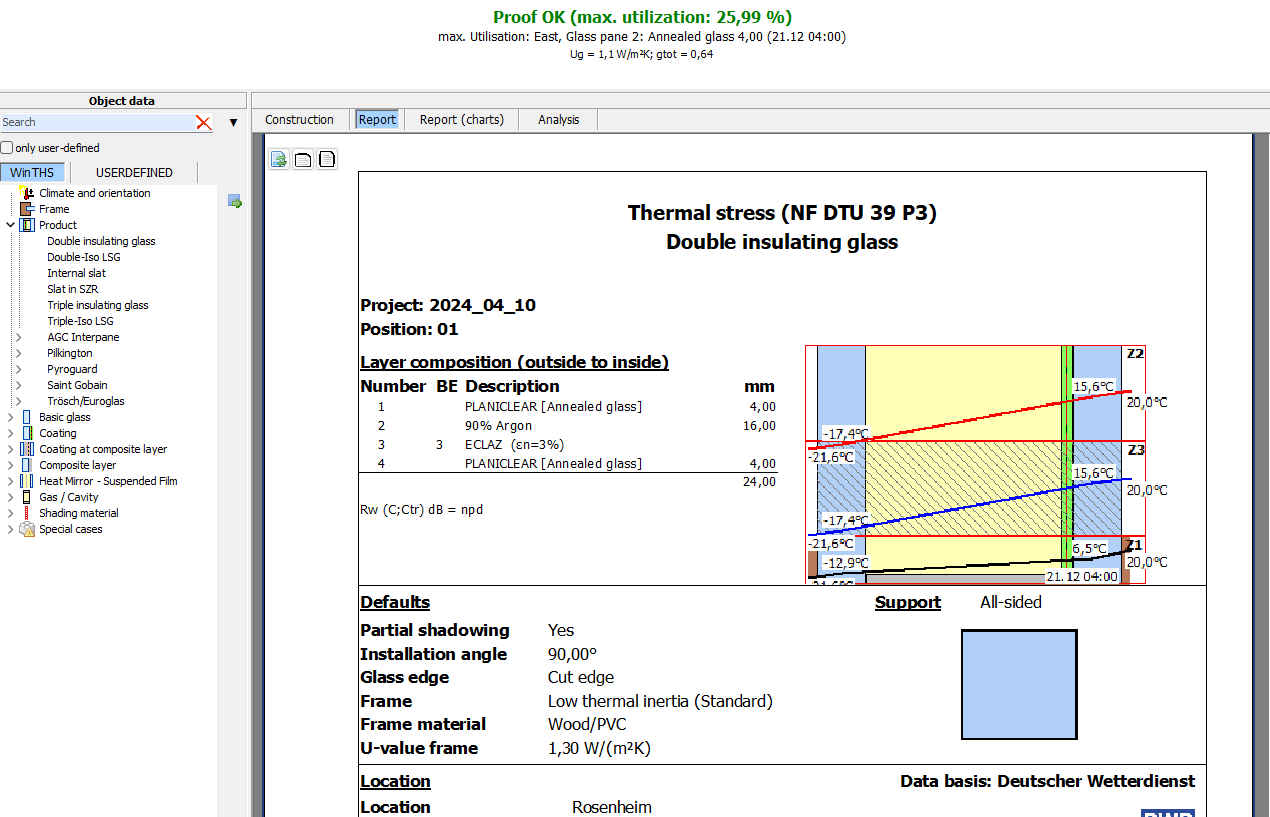
Result
- Result printout
A clear result printout displays all values at a glance - Graphical display
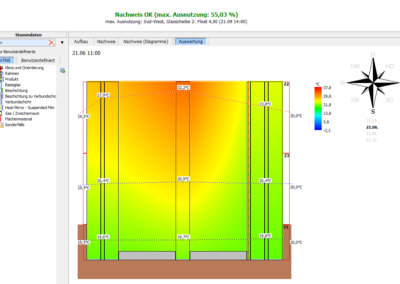
The graphical display of the glass structure with the layer temperatures simplifies the evaluation of the data - Result
The result of the verification and the maximum utilisation are displayed clearly and simply - Display of temperature distribution
Temperature distribution of the 3 zones under consideration can be visualized for each orientation and each time period in curve form or false color display.
Further variants & functions
- Save local calculations from SommerGlobal in the cloud
- Retrieve calculations from the cloud regardless of location
- Load and edit items anytime and anywhere
- View proofs as mobile documents
- Manual storage by the user
- Encrypted data
Test our demo version!
Explanation of terms

Climate and orientation

Partial shading

Frame

Result